Joshua Wolf, DDS a, Adam Weiss, DDS a, Harry Dym, DDS a,b
a. Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, The Brooklyn Hospital Center, 121 Dekalb Avenue, Brooklyn, NY 11201, USA
b. Department of Dentistry, The Brooklyn Hospital Center, 121 Dekalb Avenue, Brooklyn, NY 11201, USA
The technological advances in temporomandibular arthroscopy and arthrocentesis have given oral surgeons a treatment for patients who have not responded to conservative and pharmacologic treatment without the surgical risks and long-term recovery of open joint surgery.
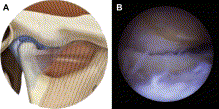
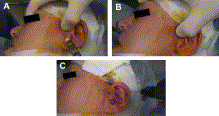
Figure 2
Figure 3
The development of a less-invasive surgical treatment of temporomandibular joint (TMJ) pathology began in 1975 when Ohnishi first used an arthoscope to enter and study the TMJ. 1 The major surgical procedures that would follow to be used with the arthroscope were diagnostic, by attaching the arthroscope to a screen to visualize the joint and the lysis and lavage of the joint (Fig. 1). This procedure most commonly involves the placement of two arthroscopic portals, one of which is for the arthroscope and the other for a blunt probe. As the joint is observed and the adhesions are encoun- tered, the probe can be used in a sweeping fashion to break up the adhesion. The use of the probe along with the hydraulic distention of the joint allow for stretching of the joint space. Images of preparation for and performing the procedure can be seen in Fig. 2. When the adhesions are broken down and the joint space distended, the joint movement improves and range of motion increases. Drugs, such as corticosteroids and sodium hyaluronate, have also been injected following the joint to reduce inflam- mation and improve lubrication, respectively. By 1991, Nitzan and colleagues showed that performing lavage of the TMJ without the scope, a procedure called arthrocent- esis, gave similar results in the reduction of pain with success rates in up to 91% of patients. 2 Arthrocentesis involves placement of two cannulas into the superior joint for hydraulic distension and joint lavage. The initial application of the procedure was...


